About HGV&TB
About HGV&TB
Tuberculosis is a major cause of mortality in the developing world. Since the establishment of genetic factors as a key player in TB, large volumes of work has been done elucidating the role of individual genes in TB susceptibility. Despite this we are far from reaching a consensus regarding the genes involved in TB susceptibility. To bring an end to this prevailing disagreement; a compilation of data on genetic variants involved in Tuberculosis susceptibility is utmost required. To date, no such systematic effort has been made in this regard.
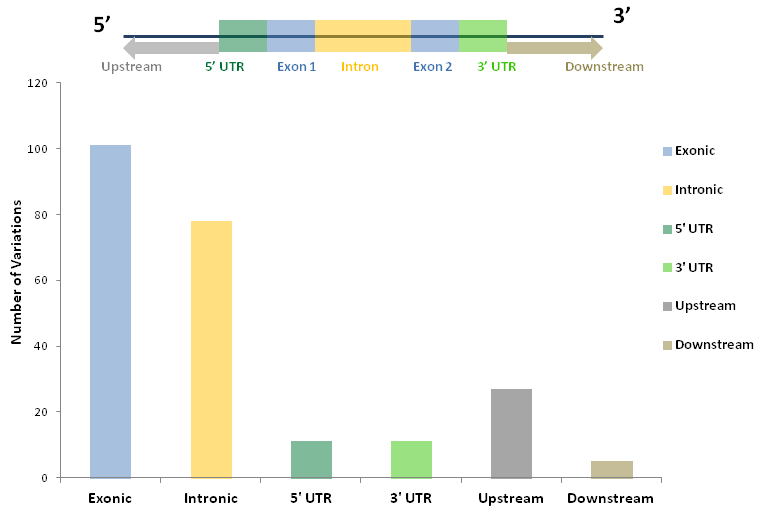
We have, thus, comprehensively curated all genetic variations reported to be associated with Tuberculosis susceptibility in human genome and established a novel Locus Specific Database that stores all Human genes and genetic variants associated with Tuberculosis (HGV&TB). The database currently house 98 genes associated with various forms of tuberculosis with 307 variants supported with pertinent patient data, obtained after an exhaustive literature study. 101 of these variations have been found to be exonic and 78 in intronic region. In addition, the database concludes the pathogenicity of the genetic variations investigated their phenotypic consequences and ethnic origin, concluding 299 genetic variants in 71 genes to be pathogenic.